Insertion Sort is an in-place sorting algorithm that succeeds in sorting smaller arrays of values, but suffers with larger arrays. Insertion Sort has a linear (O(n)) best-case permormance, which makes it useful for adding additional items a sorted array that's already sorted.
How it works?
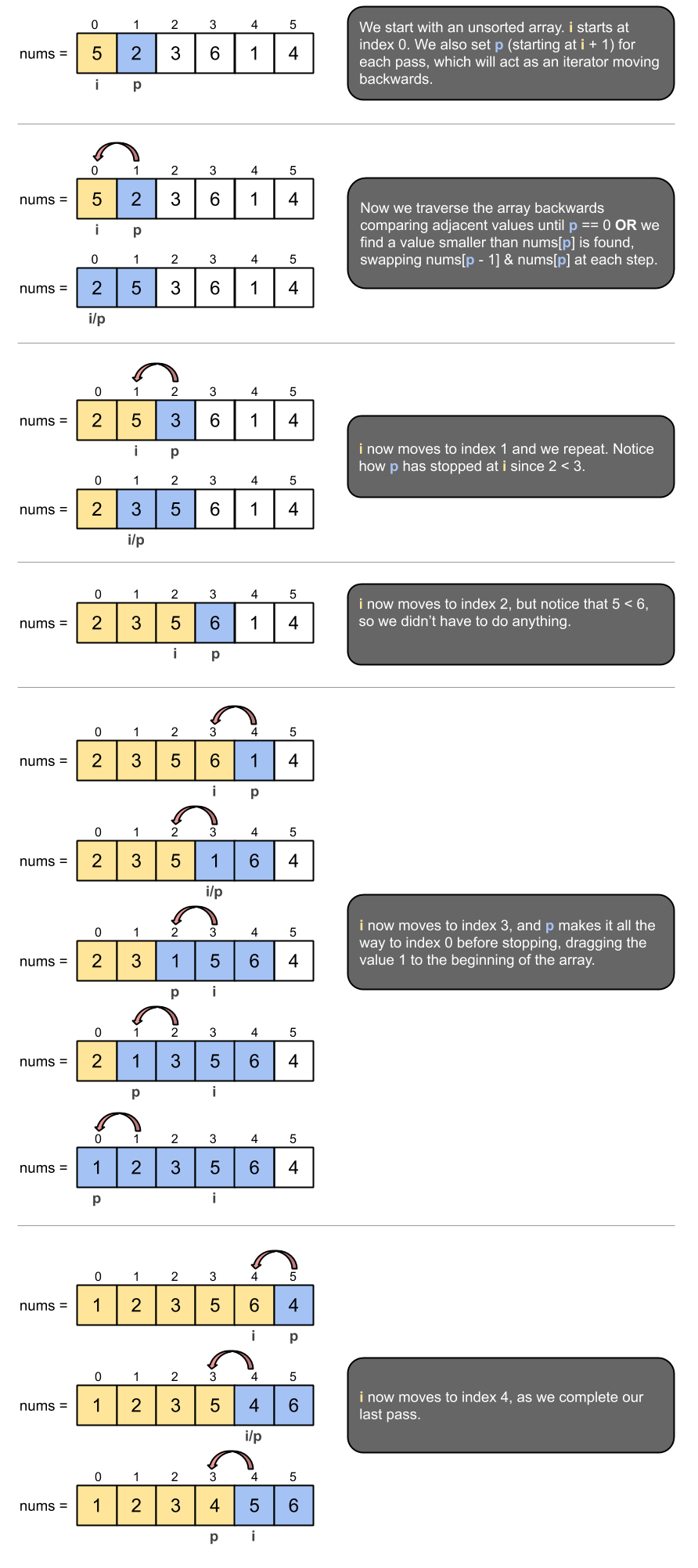
When you want to sort an existing, unsorted array use Insertion Sort by traversing the array starting at index 0 (marked by i) and then selecting a pivot (p = i + 1). You then traverse backwards from the pivot (p) either until reaching index 0 or a value larger than the pivot, swapping adjacent values in the process.
Implementation
def insertionSort(nums: list) -> list:
for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
p = i + 1 # pivot
while p > 0 and nums[p-1] > nums[p]:
nums[p-1], nums[p] = nums[p], nums[p-1]
p -= 1
return nums
print(insertionSort([5, 2, 3, 6, 1, 4]))
# => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Visual Representation
Analysis
Insertion Sort works well for small datasets or when introducing new values into an already sorted array. It also benefits from being an in-place sorting algorithm, with minimal memory used.
Time:
Worst: O(n^2)
Best: O(n) - when array is already sorted
Average: O(n^2)
Space: O(1) - swapping in place
Further Reading
Insertion Sort - Wikipedia article on Insertion Sort.
